
Title:
Author:
岡崎甚幸
Publication/Publisher:
日本建築学会論文報告集 第283号 昭和54年9月
Abstract:
この研究は,建築空間における歩行を中心とした人間行動の詳細なモデル化を試みるものである.
建築空間を一つのネットワークに抽象化し,その線上を移動する量として人間行動を調べるのでなく,建築空間を平面図形として表し,その中における各歩行者の情報を計算機に入力して,歩行者の動きを調べたり,計画中の建築空間内での平常時の歩行や避難行動が予測可能なモデルである.このモデルの最終目標は非常時の常識では考えられない人間行動の解明にある.
本モデルは,各種の磁場から任意の歩行者Iに働く磁力の緩和によって,Iの速度,単位時間後の移動距離や位置等を求めることにより,歩行者の行動をシミュレートする.
The principal objective of the research
is to develop a model of pedesirian behavior in architectual space.
In this model, behavior is not taken for movement on a schematic
architectual network, but for independent movement in real architectual
space of each pedestrian given his own attibutes. The plan of
the building, movement during rush hour or of evacuation, and
fire are displayed on the computer's Cathod Ray Tude (CRT). Pedestrian
movement is mainly caused by the application of magnetic models
and equation of motion. As it is already known, there are two
kinds of magnetic poles, namely, one with negative magnetic charge
and the other with positive. Two poles with the same charge repel
each other while those with different charge attract with a force
proportional to the product of the magnitude of the charges and
inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
In accordance with the equation of motion, F=MX, an object of
weight M moves with accelerated velocity X, being influenced by
a force F. Therefore, supposing that an object with a magnetic
pole is influenced by a force from another pole, the object moves
with accelerated velocity. The velocity of the object increases
as the force continues to act on it. The upper limit of velocity
is thus established. This motion is compared to pedestrian movement.
Each pedestrian with a positive magnetic charge, being attracted
by 'an attraction', with a negative magnetic charge, as his destination
of movement, walks avoiding other pedestrians or 'obstructions'
such as walls with positive magnetic charges. That is, a pedestrian
and an attraction attract each other, while at the same time a
pedestrian and another pedestrian and an obstruction repel one
another.
Title:
Author:
岡崎甚幸
Publication/Publisher:
日本建築学会論文報告集 第284号 昭和54年10月
Abstract:
「その1:磁気モデルの応用による歩行モデル」により,数人の歩行者が互いに対向回避する歩行や柱を回避する歩行がほぼ再現できた.しかし,他の歩行者が通り過ぎるのを待ち合わせたり,高密度の集団が出入口に殺到したり,対向したりする場合の各歩行者の動きは十分再現できない.
そこで,高密度な群集歩行における歩行者相互または歩行者と障害物の重なりの補正を行なう事により,他の歩行者を待ち合わせたり,他の歩行者の後を歩いて混雑を避ける等の高度な歩行が再現可能になった.
The simulation model of pedestrian movement
presented in the previous report stating that a position of any
pedestrian 'I' in each simulation time was dependent on the magnetic
force from all attractions, obstructions and other pedestrians.
However, the model was not sufficiently elaborate to represent
consentrated movement of pedestrians. The following model therefore,
is complementary to the above mentioned model. As shown in Fig.
1, this model consists of two different corrections; one is the
correction of overlapping between pedestrians, avoiding and passing
other pedestrians; the other one is that of overlapping between
a pedestrian and an obstruction.
Title:
Author:
岡崎甚幸
Publication/Publisher:
日本建築学会論文報告集 第285号 昭和54年11月
Abstract:
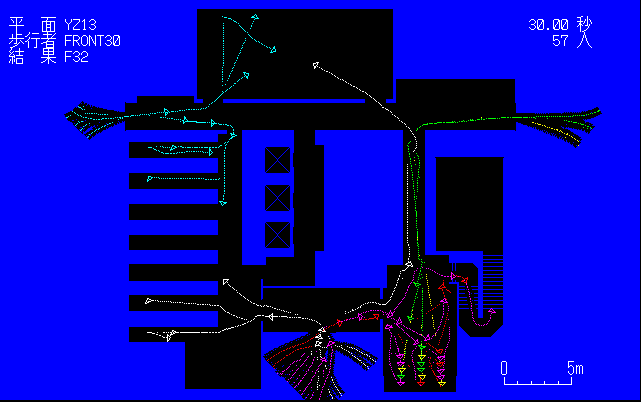
本研究は,複雑な平面をした地下街や大規模な建物における歩行のためのシミュレーションモデルの研究である. まず,歩行の最終目的地までにとりうる複数ある経路の中で最も近いものを選び,それに従って歩くためのモデルを考える.続いて,この建築空間に火災が発生した場合の,火災の発生地点における煙の広がり,避難経路が煙に覆われた場合あるいは歩行者の停滞があった場合の経路の選択などによる歩行シミュレーションモデルについて考える.
このモデルにより,火災の発生や煙の広がり,火災の成長度,歩行者の停滞,各歩行者の知らない領域,緊急時の窓からの脱出等を考慮しながら避難する歩行が再現できた.
This is a study of the simulation model
for pedestrians moving through complex architecture space such
as underground shopping malls or a building with many pedestrians.
Two theories are examined in this simulation model. One is for
movement along the shortest path to a specific destination. The
other one is for the selection of evacuation paths, taking the
generation of a fire, smoke, congestion of pedestrians and unrecognized
space into account.
Title:
Author:
岡崎甚幸、山本 親
Publication/Publisher:
日本建築学会論文報告集 第299号 昭和56年1月
Abstract:
「建築空間における歩行のためのシミュレーションモデル」によりシミュレーション中の歩行領域や歩行者の様子を,歩行者の視点から見た透視図として表現する.
これにより,以下の諸問題解決の一助にするものである.
1:火災の中を多数の歩行者がパニック状態で逃げ惑う様子や混雑の様子を恰もその中にいるように感じ取ること.2:平面状で行われた基本的な歩行シミュレーションを3次元画像に表現し,その中の歩行者の微妙な動きを観察することにより,歩行モデルの妥当性を検討すること.3:駅舎内の壁や柱の位置,誘導標の位置,そこを通過する群集等が移動中の歩行者にどのように見えるか調べ,建築空間の設計計画に役立てること.
This is a study of computer simulation model
that made it possible to display perspective view of pedestrian
movement in architectural space on computer's Cathod Ray Tube
as well as plan of them. As perspective is viewed from one of
pedestrians who walk according to this model, operator feels as
if he walked through the architectural space as a pedestrian or
escaped through an exit considering spreading smoke. Architectural
space designed and delicate pedestrian movement are also examined
in simulation respectively to improve its design and algorism
of movement.
Title:
Author:
岡崎甚幸、松下 聡
Publication/Publisher:
日本建築学会論文報告集 第302号 昭和56年4月
Abstract:
探索歩行および誘導標による歩行が可能なシミュレーションモデルの研究である.
探索歩行は,前もって決められている経路を歩行者が歩くのではなく,各シミュレーションにおいて歩行者独自の判断によって,歩行領域の特性に従いつつ,未知の歩行領域を進むものである.そして,目的領域を発見すると探索歩行は完了する.
誘導標による歩行とは,探索歩行の途中で誘導標を提示し歩行者を正しい方向に導くものである.このモデルにより,計画中の駅舎の平面において誘導標の適正配置を調べるための歩行シミュレーション等が可能になる.
This is a study of computer simulation model
of a proubing walk and a guide walk displaying the pedestrian
movement and the plan of building as pedestrian field on the Cathod
Ray Tube. The pedestrian field is surrounded by polygonal line
which is composed of vectors indicating walls. A node of two wall
vectors, that is convex into the pedestrian field is a corner
of pedestrian field. A pedestrian walks proubing the appropriate
corner where he turns to walk to another appropriate corners until
he fields his destination field unit. A guideboard, indicating
the number of one of destination field unites and the direction
to the unit, helps a pedestrian to choose the appropriate corner.
The model made the pedestrian movement in, the maze and movement
in the station with guideboards possible.
Title:
Author:
岡崎甚幸、松下 聡
Publication/Publisher:
日本建築学会論文報告集第436号, 49-58頁(1992年), 1992年 6月
Abstract:
群集歩行シュミレーションによって防災評定避難計算と同一条件で、与えられた平面上でシュミレーションを行い、防災評定避難計算の結果およびその他以下に述べる種々の検討が可能であることを示す。防災評定避難計算で行っている数値計算とグラフによる避難特性の表現ではなく、ここの避難者の行動を時事刻々画面上に表示し、建築空間の全体的、部分的な避難特性を視覚的に把握可能にする。またシュミレーション結果から、必要な任意の時刻における出入口や通路の流動係数や歩行速度が測定可能なので、プログラムが正式に作動しているか田舎を用意に検討できる。
This is a proposal of an application method
of simulation model for pedestrian movement to evaluation of building
plans regarding fire escape. The model visualize the movement
of each pedestrian in building plans, so designers can easily
find problems of plans to improve them 11 examples of simulation
show that this model is available for evalution of fire safty
of plans as well as existing calculation method, and that the
model is available for other roblems like changes of coeffocient
of pedestran flow and change of path. The accuracy of the model
is confirmed by experiments of pedestrian movement.
Title:
Author:
岡崎甚幸、松下 聡
Publication/Publisher:
Proceeding of the International Conference on Engineering for
Crowd Safety,P.271-280,1993
Abstract:
The objective of this study is the development of a computer
simulation model for pedestrian movement in architectural and
urban space. The characteristic of the model is the ability to
visualize the movement of each pedestrian in a plan as an animation.
So architects and designers can easily find and understand the
problems in their design projects. In this model, the movement
of each pedestrian is simulated by the motion of a magnetized
object in a magnetic field. Positive magnetic pole is given to
each pedestrian and obstacles like walls and columns. Negative
magnetic pole is located at the goal of pedestrians. Each pedestrian
moves to his goal by the attractive force caused by the negative
magnetic pole at his goal, avoiding collisions with other pedestrians
and obstacles by repulsive forces caused by the positive magnetic
poles. The effectiveness of the simulation model is shown by the
following two kinds of simulation examples. (1) Evacuation from
an office building In this model pedestrians walk along the route
from each starting point to the exit in case of evacuation. The
example shows the places where stagnations and heavy congestions
occur, and designers can see if the evacuation routes are appropriate.
(2) Movement of pedestrians in queue spaces Three types of queuing
behavior is classified in this model: movement in front of counters,
movement passing through ratches, and movement of getting on and
off in elevator halls. Simulation examples in a railway station
and in a main floor of a resort hotel are shown where several
kinds of queue spaces are included and complicated movements of
hundreds of pedestrians occur.